MY VASCULAR HEALTH
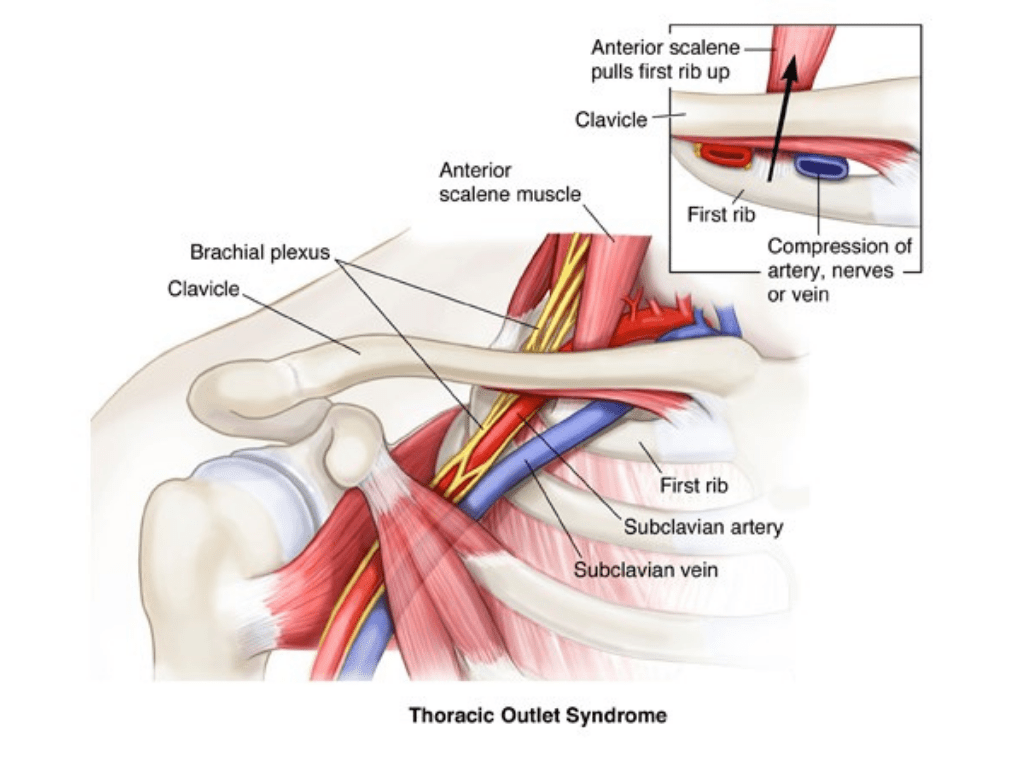
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Overview
The small space in the upper chest and shoulder between the collarbone and the first rib is called the Thoracic outlet area. There are muscles, nerves, and blood vessels in this region which lead down the arm to the hand. In some people, the space is narrowed which puts pressure on the nerves or blood vessels. This is called Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS).
Signs & Symptoms:
- Swelling in the arm
- Weakness in the arm or hand which may worsen when the arm is raised over the head
- Pain, numbness or tingling in the arm or hand
Treatment Options:
The treatment of thoracic outlet syndrome depends on its presentation; neurogenic TOS results from compression of the nerves, venous TOS results in DVT in the axillary subclavian vein from compression and repetitive injury, and arterial TOS results from compression of the arteries.
The neurogenic TOS is most often treated with physical therapy and sometimes requires surgical resection of the first rib and scalene muscles. The venous TOS requires immediate attention; treatment includes blood-thinners, catheter-directed thrombolytic therapy to dissolve the clot, and often followed by resection of the first rib and scalene muscles. Lastly, arterial TOS often requires resection of the first rib and scalene muscles and possible repair of the damaged artery.